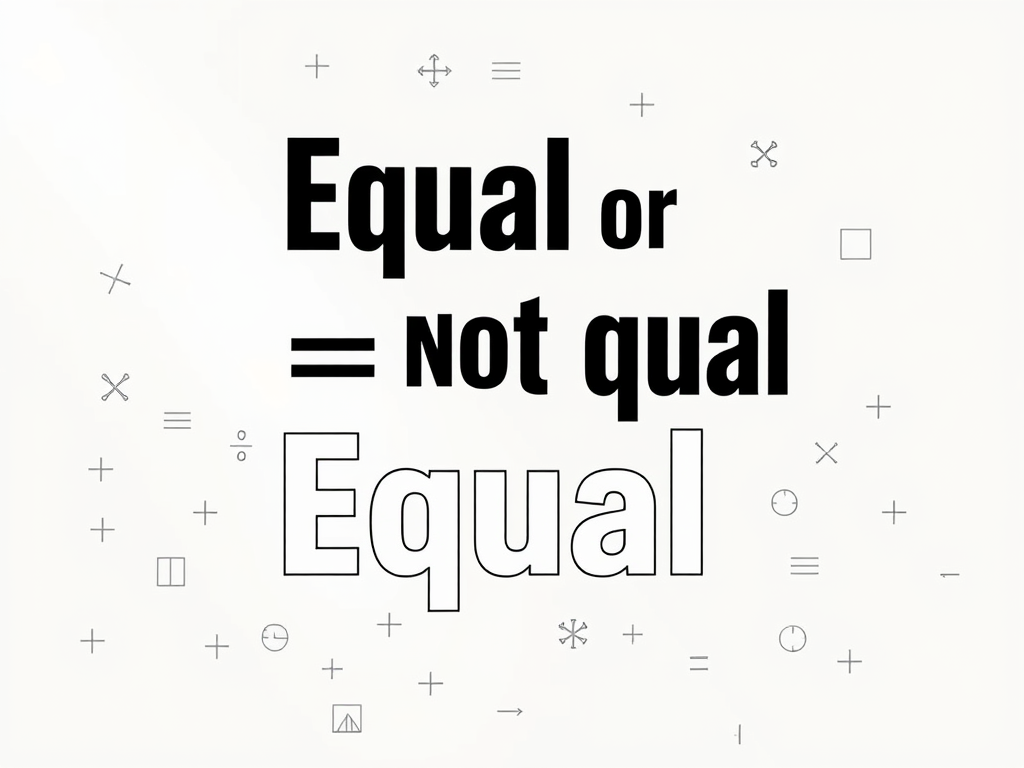The content presents a higher complexity math set including multiple-choice questions, short answer problems, and a case study. Key topics encompass algebra, geometry, temperature calculations, and speed, while the case study focuses on scoring in a competitive exam scenario. Solutions and methods are outlined in detail, emphasizing algebraic reasoning.
CLASS 7 MATH QUESTION PAPER – SET 5 (Corrected – Same Complexity) TOPICS: Number play, Geometric twins, Operations with integers, Another peek beyond the point.
The content is a corrected question paper comprising multiple-choice, short answer, long answer questions, and a case study, focusing on topics like number play, geometry, and operations with integers. It includes problems involving angles, temperature changes, car mileage, and triangle congruency, along with respective answer keys for grading.
CLASS 7 MATH Question Paper Set 4 – Higher + Application + Logical Reasoning – TOPICS: A Tale of three intersecting lines, Arithmetic Expressions, Expressions using letter numbers.
The content outlines a mathematics exercise set focusing on higher-level applications and logical reasoning, covering triangles, arithmetic expressions, and age-related problems. It includes multiple sections with various problems requiring simplification, equation formation, and proof. Solutions are provided, demonstrating the concepts effectively.
CLASS 7 MATH Question Paper Set 3 – Higher Complexity – TOPICS: A Tale of three intersecting lines, Arithmetic Expressions, Expressions using letter numbers.
The content discusses a set of problems involving triangles, arithmetic expressions, and algebraic simplifications. It includes questions on identifying triangle sides, calculating twin primes, simplifying expressions, and constructing triangles. Additionally, it features a case study examining conditions for triangle formation and explores inequality properties, providing detailed solutions and answers for each section.
Class 7 – DECIMALS PRACTICE WORKSHEET – SET 2
This mathematics practice worksheet for Class 7 includes multiple-choice questions and problem-solving exercises focused on decimal operations, conversions, calculations involving costs, and geometry. It also features a case study about calorie calculations and gym membership costs. The answer key provides solutions for verification.
Class 7 – DECIMALS PRACTICE WORKSHEET – SET 1
The Class 7 Decimals Practice Worksheet includes multiple-choice questions on decimal operations, practical problems involving distance, cost, and area calculations, and case study-based queries about protein intake. Each section offers various mathematical challenges to enhance students’ understanding of decimals and related concepts in mathematics.
CLASS 7 – MATH QUESTION PAPER – SET 2
The Class 7 Mathematics question paper for the annual examination includes various topics such as arithmetic expressions and geometry. It features multiple-choice questions and problem-solving sections, covering concepts like triangle inequalities, age problems, and algebraic contributions. The content also requires students to construct triangles and apply geometric theorems.
CLASS 7- MATH QUESTION PAPER – SET 1
📘 CLASS 7- MATH QUESTION PAPER – SET 1 ANNUAL EXAMINATION (2025–2026)SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS Contains Questions from below chapter Ch.2 Arithmetic ExpressionsCh.4 Expressions using Letter-NumbersCh.6 Number […]
Class 7 – EXPRESSIONS USING LETTERS-NUMBERS
The content covers a practice paper for Class 7 focused on algebraic expressions using letters and numbers. It includes multiple-choice questions involving geometric shapes, simplification of expressions, calculation of costs, and case studies related to travel expenses and date grids. Students are asked to derive expressions and compute values based on given scenarios.
📘 Class 7 पत्र लेखन – औपचारिक और अनौपचारिक पत्र (Examples Included)
The content discusses letter writing for Class 7 Hindi, emphasizing the importance of both formal and informal letters. It provides various examples, including letters to friends and authorities on different subjects like personal achievements and community issues. The examples are presented in simple language to aid understanding.
Class VII Science – Nutrition in Animals
The content comprises a question bank for a Class VII Science lesson on animal nutrition, featuring multiple-choice questions, oral questions, worksheets, and true/false statements. It explores various aspects of digestion, absorption, and food processing in animals, including specific questions about teeth types, digestive glands, and processes involved in nutrition.
Class 7 – Subject and Verb Agreement Worksheets with Answers
The lesson covers the concept of Subject and Verb Agreement, indicating that verbs must match their subjects in number and person. It includes exercises focused on various indefinite pronouns and sentence structures to reinforce this grammar rule. Each exercise is followed by an answer key for self-assessment.
Class VII – Arithmetic ExpressionsPractice Paper
The content consists of a practice paper for Class VII focusing on arithmetic expressions. It includes multiple-choice questions, fill-in-the-blanks, evaluation of expressions, and case studies involving real-life scenarios. Students practice concepts like order of operations, properties of multiplication, and formulating numerical expressions, while also solving related problems.
Cut Drill 2 🏏 Full toss on off side, Duggu & Dakshu play clean cut shots
12-year-old Duggu and 10-year-old Dakshu practice clean cut shots during cricket drills, specifically focusing on full tosses on the off side. This training emphasizes their batting skills in a fun, engaging way. The session highlights the importance of cut shots in developing young cricket players’ techniques.
Day 2 | Word of the Day: Monotony — lack of variation, tediously the same. #day2 #1500days1500words
The word of the day for Day 2 is “monotony,” defined as a lack of variation and a state of being tediously the same. This entry is part of the #1500days1500words challenge.
Availability vs Reliability — System Design Concept (Simple Guide)
Availability and reliability are critical concepts in system design. Reliability measures how consistently a system operates without failure, while availability assesses its operational status when needed. An ideal design balances both, aiming for fault tolerance and quick recovery to ensure systems remain usable, even amid failures.
System Design Concepts – Availability
Availability measures the accessibility and proper functioning of a service, usually expressed as a percentage. High availability is crucial for user experience, business continuity, and compliance. Calculated by total time minus downtime, availability levels, indicated by “nines,” inform reliability. Understanding availability helps businesses improve systems and select reliable providers.
Cut Drill #1 – Catch, set and cut 🔥 Duggu & Dakshu sharpening cut shots with drills 🏏 #cricketdrills
Cut Drill #1 – Catch, set and cut 🔥 Duggu & Dakshu sharpening cut shots with drills 🏏 #cricketdrills
Day 1 of 1500: Mercurial — quick minds, shifting moods & beautiful unpredictability ✨ #WordOfTheDay
1500 Days | 1500 Words 📖 Day 1 begins with Mercurial — a word that captures quick thinking, sharp wit, and unpredictable moods. One word […]
Algebraic Expressions Practice – 12 Questions with Answers | Class 7 & 8 Maths
Boost your Algebra skills with this set of 12 well-designed questions covering expression formation, simplification, perimeter formulas, cost expressions, and real-life word problems.
Perfect for Class 7 and Class 8 students looking to strengthen their understanding of algebraic expressions.
This post includes:
Easy, Medium & Higher-Level Questions
Fully worked-out Answer Key
Concept-based practice for school exams & homework
Student-friendly explanations
Ideal for teachers, parents, and students preparing for CBSE Class 7 & 8 Maths.
Algebraic Expression Practice Questions with Answers | Class 7 & 8 Maths
Strengthen your Algebra skills with these 15 carefully-designed practice questions based on algebraic expressions.
Covers real-life word problems, cost expressions, simplification, and forming algebraic expressions using variables.
Perfect for Class 7 and Class 8 students preparing for exams, worksheets, and revision.
This post includes:
✓ Word problems
✓ Algebraic expressions
✓ Simplified answers
✓ Easy to understand solutions
Use this to revise concepts quickly or practice for school tests!
Class 7 – Simplify Algebraic expression
The content provides a series of algebraic expressions categorized by difficulty levels: easy, medium, and hard. Each expression is simplified step-by-step, showcasing the process of combining like terms and applying arithmetic operations. An answer key is included, offering the final simplified forms of each expression for reference.
Class 7 Math Worksheet: Triangles & Right-Angled Triangles with Solutions
Boost your Class 7 students’ understanding of triangles with this comprehensive worksheet! Includes 19 multiple-choice questions on right-angled triangles, Pythagoras theorem, triangle inequalities, and angles. Each question comes with clear diagrams and a detailed answer key for step-by-step learning. Perfect for classroom practice, homework, or self-study.
Class 7 : 30 Challenging Algebra & Expression Problems for Students – Cut, Divide & Solve!
Boost your algebra skills with these 30 carefully designed expression-based problems! From simple rope and ribbon cuts to complex multi-step operations, these questions test your ability to create and simplify expressions. Perfect for middle and high school students preparing for exams or competitive quizzes.
Practice solving for lengths, divisions, folds, additions, and fractions with step-by-step logical reasoning. Test yourself and see how fast you can calculate!
BODMAS Practice Questions for Class 7 & 8 | Mixed Operations Worksheet
Boost your calculation skills with this curated set of BODMAS questions including brackets, division, multiplication, addition, subtraction, and the “of” operator. Perfect for Class 7 and 8 students to strengthen speed and accuracy in arithmetic.
Includes 23 mixed-difficulty questions and a complete answer key for quick self-check!
Arithmetic Expressions – Equal or Not Equal
Sharpen your mental math skills with these quick simplification and equivalence questions. Each problem gives you an expression, and your task is to identify which option does not match its value. These questions help strengthen number sense, subtraction fluency, and the ability to compare expressions without fully solving each one. Perfect for Class 6–8 students preparing for exams or practicing daily math reasoning!
Class 7 Fractions MCQ Worksheet with Answers | Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction & Division
Practice important Class 7 Maths concepts with this Fractions MCQ worksheet. Covers multiplication, addition, subtraction, and division of fractions with multiple-choice questions. Answer key provided for easy revision and self-assessment.
Reciprocal of Fractions – Class 7 Questions and Answers
Practice important Class 7 math questions on reciprocals of fractions. Includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs) with answers on proper fractions, improper fractions, mixed fractions, and whole numbers to strengthen conceptual understanding.
Geometry MCQs with Answers – Parallel Lines, Angles, Triangles, and Polygons
Practice a set of 25 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) on geometry covering parallel and perpendicular lines, types of angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and polygons. Includes an answer key for quick self-assessment. Perfect for students and teachers preparing worksheets or exams.
हिंदी व्याकरण – वचन की परिभाषा, प्रकार और उदाहरण
इस पेज पर वचन की परिभाषा, उसके प्रकार (एकवचन और बहुवचन), दोनों के बीच अंतर तथा शब्दों के वचन बदलने के उदाहरण दिए गए हैं। विद्यार्थी और प्रतियोगी परीक्षा की तैयारी करने वालों के लिए यह सामग्री उपयोगी है।
वे दिन भी क्या दिन थे – प्रश्न उत्तर, शब्दार्थ और अभ्यास | कक्षा 5 हिंदी
वे दिन भी क्या दिन थे – प्रश्न उत्तर, शब्दार्थ और अभ्यास | कक्षा 5 हिंदी
कक्षा 5 हिंदी पाठ 8 “वे दिन भी क्या दिन थे” के शब्दार्थ, प्रश्न उत्तर, वाक्य निर्माण और नैतिक प्रश्न। विद्यार्थियों के लिए संपूर्ण अभ्यास सामग्री।
कारक (Case) – हिंदी व्याकरण | परिभाषा, भेद, उदाहरण और अभ्यास प्रश्न
कारक (Case) – हिंदी व्याकरण | परिभाषा, भेद, उदाहरण और अभ्यास प्रश्न
सर्वनाम प्रश्नोत्तरी – कक्षा 5 हिंदी व्याकरण अभ्यास
कक्षा 5 हिंदी व्याकरण के लिए सर्वनाम पर आधारित महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न और उत्तर। रिक्त स्थान भरिए, वाक्य पुनर्लेखन, सर्वनाम की पहचान और अभ्यास हेतु वर्कशीट उपलब्ध। बच्चों की पढ़ाई और परीक्षा तैयारी के लिए उपयोगी।
एक माँ की बेबसी – कक्षा 5 हिंदी प्रश्नपत्र | Hindi Worksheet Class 5
कक्षा 5 हिंदी पाठ 9 – ‘एक माँ की बेबसी’ का प्रश्नपत्र और वर्कशीट। शब्दार्थ, प्रश्न-उत्तर, रिक्त स्थान, नैतिक प्रश्न तथा अभ्यास प्रश्नों के साथ परीक्षा की तैयारी के लिए उपयुक्त सामग्री।
वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द | One Word Substitution in Hindi for Class 5-6
वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द | One Word Substitution in Hindi for Class 5-6
कक्षा 5 और 6 के छात्रों के लिए हिंदी व्याकरण अभ्यास – वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द (One Word Substitution)। आसान उदाहरण, प्रश्न-उत्तर और वर्कशीट बच्चों की परीक्षा तैयारी और अभ्यास के लिए।
विज्ञापन लेखन वर्कशीट – कक्षा 5 | Advertisement Writing Worksheets in Hindi
विज्ञापन लेखन वर्कशीट – कक्षा 5 | Advertisement Writing Worksheets in Hindi
कक्षा 5 के छात्रों के लिए विज्ञापन लेखन वर्कशीट। आसान और रचनात्मक विज्ञापन जैसे कलम, साइकिल, पुस्तक, घड़ी आदि के उदाहरण और उत्तर। बच्चों के लिए हिंदी भाषा का अभ्यास।
कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण – उपसर्ग और प्रत्यय अभ्यास प्रश्नोत्तर (Set 1 से 4)
Practice Class 7 Hindi Grammar with Upsarg (Prefixes) and Pratyay (Suffixes) exercises. Includes 4 sets of solved questions – make words using prefixes/suffixes, separate root word, and identify upsarg-pratyay. Perfect for revision and exam preparation.
कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण – क्रिया (Verb) अभ्यास प्रश्नोत्तर Set 1 से 4
Practice Class 7 Hindi Grammar with Kriya (Verb) exercises. Includes 4 sets of solved questions – correct verb forms and identify Sakarmak/Akarmak verbs. Perfect for revision, homework, and exam preparation.
कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण – काल (Tense) अभ्यास प्रश्नोत्तर Set 1 से 4
Practice Hindi Grammar for Class 7 with Kaal (Tense) exercises. Includes 4 sets of solved questions – identify verbs, write tense, and change sentences into Present, Past and Future tense. Useful for revision, homework, and exam preparation.
कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण – विशेषण अभ्यास प्रश्नोत्तर (Set 1 से 3)
Practice Hindi Grammar for Class 7 with Visheshan (Adjective) Exercises. Includes 3 sets of questions with answers – fill in the blanks, identify adjectives and correct sentences. Perfect for revision and exam preparation.
विशेषण अभ्यास प्रश्नोत्तर – कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण (Set 1–5)
Download Class 7 Hindi Grammar Worksheet on Visheshan (Adjectives). Contains 5 sets of practice questions with answers – fill in the blanks, identify, and write adjectives. Perfect for revision and exam preparation.
Fill in the Blanks – सर्वनाम अभ्यास प्रश्न (Class 7 Hindi Grammar)
सर्वनाम (Pronoun) पर आधारित Fill in the Blanks प्रश्न अभ्यास करें। कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण के लिए उपयुक्त वर्कशीट – सही सर्वनाम चुनकर रिक्त स्थान भरें। परीक्षा तैयारी के लिए आदर्श अभ्यास प्रश्न।
संज्ञा शब्दों को सर्वनाम से बदलकर वाक्य – अभ्यास प्रश्न
संज्ञा शब्दों को सर्वनाम से बदलने के अभ्यास प्रश्न पढ़िए। कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण के लिए महत्वपूर्ण उदाहरण – राम, सीमा, मोहन, सोहन और अन्य वाक्यों में संज्ञा को सर्वनाम से बदलकर लिखिए।
📘 सर्वनाम शब्दों के वाक्य – कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण अभ्यास
सर्वनाम शब्दों के वाक्य (Pronoun Sentences in Hindi) के सुंदर उदाहरण – मैं, हम, तुम, आप, वह, यह, वही, कोई, सब, जो, जैसा आदि। कक्षा 7 हिंदी व्याकरण अभ्यास के लिए उपयोगी वाक्य संग्रह।
सर्वनाम से प्रश्न – Set 1, Set 2 और Set 3 (Class 7 Hindi Grammar Practice)
हिंदी व्याकरण के महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्नों का संग्रह – सर्वनाम की परिभाषा, प्रकार, भेद और उदाहरण। Set 1, Set 2 और Set 3 में दिए गए प्रश्नों से अभ्यास करें और सर्वनाम को सरलता से समझें। यह सामग्री कक्षा 6, 7 और 8 के विद्यार्थियों के लिए उपयोगी है।
हिंदी व्याकरण अभ्यास प्रश्न – संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, क्रिया, विलोम, पयायवाची
Class 7 Hindi Grammar Practice Worksheet – संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, क्रिया, विलोम, पयायवाची और विज्ञापन लेखन पर आधारित प्रश्न। परीक्षा की तैयारी के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हिंदी व्याकरण अभ्यास प्रश्न।
Class 5 Computer Science Revision Worksheet – Networking Basics – Multiple Choice & Descriptive Questions (Set 3)
Practice Set 3 of Internet and networking questions with MCQs and descriptive answers. Covers IP address, DNS, HTTP, routers, cloud storage, hubs vs switches, and how websites load. Useful for students and competitive exams.
Class 5 Computer Science Revision Worksheet – Networking Basics – Multiple Choice & Descriptive Questions (Set 2)
Explore Set 2 of computer networks questions with MCQs and descriptive answers. Topics include PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN, wired vs wireless communication, cloud computing, and networking advantages. Ideal for exams and practice.
Class 5 Computer Science Revision Worksheet – Networking Basics – Multiple Choice & Descriptive Questions (Set 1)
Practice important networking basics with Set 1 of multiple-choice and descriptive questions. Covers wired vs wireless networks, LAN, WAN, Internet history, and data transfer steps. Perfect for students and exam preparation.
Class 5 Computer Science Revision Worksheet – Hardware, Software, System Software & Stepwise Tasks
Prepare for Class 5 Computer Science exams with this comprehensive revision worksheet. Covers hardware and software, system software, operating systems, stepwise tasks like creating folders, restarting computers, and using application software. Includes multiple-choice, fill-in-the-blanks, descriptive, and research-based questions.
Class 5 Computer Science Revision Worksheet | Computer Networks & Internet
Prepare for Class 5 Mid Term Computer Science exams with this revision worksheet covering Computer Networks, Internet, and its services. Includes fill-in-the-blanks, multiple-choice, matching, and diagram-based questions.
Chapter 4 – Very Able Variables | Python Class 7 MCQs, Exercises & Programs – Set 3
Boost your Python skills with this high-difficulty set of Chapter 4 “Very Able Variables” questions. Includes tricky MCQs, fill-in-the-blanks, and descriptive questions with answer keys – perfect for Class 7 exam preparation.
Chapter 4 – Very Able Variables | Python Class 7 MCQs, Exercises & Programs – Set 2
Practice Chapter 4 – Very Able Variables for Class 7 Python with MCQs, fill-in-the-blanks, descriptive questions, and coding exercises. Topics include variable naming rules, assignment vs comparison operators, data types (int, float, str), exponentiation, floor division, and input/output programs. Perfect for exam prep and hands-on practice.
Chapter 4 – Very Able Variables | Python Class 7 MCQs, Exercises & Programs – Set 1
Practice Python Class 7 Chapter 4 – Very Able Variables with MCQs, fill-in-the-blanks, descriptive questions, and programming exercises. Topics include valid variable names, arithmetic operators, input functions, type casting, integer and floor division, and Python naming rules. Ideal for exam prep and coding practice.
Python Class 7 Practice Questions SET 2 – If Condition, Loops, Range & Programming Exercises
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS FILL IN THE BLANKS DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS PROGRAMMING QUESTIONS
Python Class 7 Practice Questions SET 1 Answer Key – If Condition, Loops, Range & Programming Exercises
Python Class 7 Practice Questions SET 1 Answer Key – If Condition, Loops, Range & Programming Exercises
Python Class 7 Practice Questions SET 1 – If Condition, Loops, Range & Programming Exercises
Boost your Python learning with this Class 7 Computer Science worksheet covering MCQs, fill in the blanks, descriptive questions, and coding exercises. Topics include if conditions, loops, range(), break & continue statements, prime number check, vowel counter, and multiplication tables. Perfect for exam prep and practice.
Class 7 Computer Science Python Application Questions | Variables, If-Else, Loops & Operators (Set 1 & 2)
Practice Python application-based questions for Class 7 Computer Science on variables, if-else, loops, and operators. Includes two sets of exam-style coding problems with real-life scenarios like discounts, eligibility checks, password strength, ticket pricing, and student marks analysis.
Computer Science – Python Class 7 – Very able Variables, If you think for a while – Practise Set 2
Prepare for exams with Python practice questions on variables, data types, if-else conditions, and while loops. Includes MCQs, fill-ups, coding questions, and syntax exercises with examples. Perfect for Class 7–8 Computer Science students.
Computer Science – Python Class 7 – Very able Variables, If you think for a while – Practise Set 1
Prepare for exams with Python practice questions on variables, data types, if-else conditions, and while loops. Includes MCQs, fill-ups, coding questions, and syntax exercises with examples. Perfect for Class 7–8 Computer Science students.
Data Interpretation Practice: Bar Chart, Tally Chart, Pictograph & Pie Chart Questions for Class 5
Practice data interpretation with Class 5 math questions: bar chart (cars produced 2015–2019), tally chart (favorite fruits), pictograph (ice cream flavors), and pie chart (favorite subjects of 120 students). Includes solved examples and questions to help kids prepare for exams.
Convert Numbers to Tally Marks and Tally Marks to Numbers | Practice
Learn how to convert numbers into tally marks and tally marks into numbers. Free worksheet examples for 1–30 with answers: 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 20, 22, 23, 27, 30. Perfect for kids, teachers, and math practice.
Math Fill-in-the-Blanks: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication & Division Practice (Class 4–6)
Sharpen your math skills with this fill-in-the-blank worksheet covering multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction. Ideal for Class 4 to 6 students preparing for exams or daily practice. Includes missing value problems and direct equations.
Fill in the blanks: Find Dividend, Divisor, Quotient & Remainder (Class 5-7)
Practice division word problems for Class 5, 6 and 7 students. Fill in missing values of dividend, divisor, quotient, or remainder using the division formula. Great for revision and exam prep.
Math Quiz: Data Handling, Averages & Unit Problems (Class 5-7)
The content consists of multiple-choice questions focusing on graph types, speed calculations, average calculations, and basic arithmetic. It tests knowledge of how to represent data visually and solve simple math problems, including determining totals and averages based on contextual scenarios involving transport and items.
Grade 5 – Mathematics: Addition, Subtraction, and Their Applications
The content presents various mathematical problems involving arithmetic operations, profit and loss calculations, and word problems. It includes original questions and similar examples for addition and subtraction, savings calculations, and determining losses from sales of items. The focus is on practical applications of mathematical concepts in everyday scenarios.
CLASS 5 MATHS – PLACE VALUE, ADDITION, SUBTRACTION AND THEIR APPLICATION
The content consists of various mathematical problems and exercises, focusing on number conversions, identifying places in large numbers, profit and loss calculations, rounding numbers, and Roman numeral recognition. It includes multiple-choice questions and similar queries aimed at reinforcing concepts related to numbers and arithmetic operations.
MATHEMATICS GRADE 5 – PRACTICE WORKSHEETADDITION, SUBTRACTION AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
1. Solve the following Original a. 23,56,899 + 4,56,777 – 4,33,231 Similar Questions: Original b. ________ – 87,378 = 9,83,473 Similar Questions: Original c. 7,54,321 […]
Mathematics Grade V – Worksheet: Addition, Subtraction and Their Applications
The content provides a series of math problems involving addition, subtraction, word problems, profit and loss calculations, selling prices, total expenses for purchases, and population changes. It includes similar questions and challenges to find missing numbers, emphasizing practical applications of basic arithmetic in everyday scenarios.
Class 5 Math – Place Value More Practise Sheet
The content presents various mathematical exercises focusing on number representation, including writing numerals in word and expanded forms, finding place values, and identifying the greatest and smallest numbers from given digits. It also covers rounding numbers, comparing numerical values, and performing calculations with Roman numerals, providing original questions alongside similar practice sets.
Class 5 Maths – PLACE VALUE
The content outlines various number-related tasks, including writing numbers in words and expanded form, finding predecessors and successors, comparing numbers, arranging them in ascending order, rounding off, and converting between number systems and Roman numerals. Each section includes original and similar questions for practice.
Fraction Word Problems for Class 7 – Practice with Everyday Math
The content outlines various scenarios involving calculations of ingredients or resources needed for tasks such as baking, making juice, filling boxes, and more. Each scenario presents a question about total requirements, sufficiency of available resources, and maximum capacity. It emphasizes practical application of fractions and basic arithmetic.
Numbers & Operations – Class 7
The task involves using numbers from a specified set (250, 600, 5,000, 9,000, 1,200, 45,000) to reach various target numbers through mathematical operations. Each number can be used only once, with target numbers including pairs such as (16,050; 39,100) and (10,200; 44,500) among others.
Fraction – Word Problem
The content presents various mathematical problems involving rates of work. It includes scenarios where a gardener, machine, printer, cook, and car complete fractions of their respective tasks in one hour. The questions ask for the amounts completed in shorter time frames, encouraging calculations of fractions based on different time intervals.
Word Problems Using Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication & Division of Fractions
The content presents various word problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with fractions. Examples include calculating total milk consumption, determining weights of fruits, and solving for remaining quantities after specific operations. The problems aim to enhance understanding and application of basic mathematical concepts related to fractions and operations.
Number System Word Problems – Class 7
The post consists of various word problems focused on basic arithmetic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Examples include calculating total collections, population changes, earnings differences, costs and production numbers, as well as equal distributions. Each problem presents a practical scenario requiring a numerical solution.
Mastering Word Problems: Numbers, Fractions & Calculator Skills – Class 7
🔢 Large Numbers – Word Problems (Class 7) 🧮 Fractions – Word Problems (Class 7) 🧠 Calculator Button Problem (Class 7 Level) 1. A calculator has buttons +1, +10, +100, […]
Class 7 Maths: Assertion and Reason Practice – Fractions & Large Numbers
The content presents a series of assertions and reasons related to fractions and numerical values, each followed by multiple-choice options evaluating the truth and explanatory relationship between the assertion and its reasoning. The focus is on mathematical concepts, definitions, and logical reasoning in a structured format.
Unitary Method Using Fractions – Word Problems for Class 7
The content presents a series of mathematical problems involving division of quantities. Each scenario details how to calculate the amount used or consumed per individual item or person, such as ribbon for badges, paint for chairs, sugar in bags, and divisions for milk, chocolate, cloth, a book, and pizza among multiple recipients.
Mastering Estimation & Operations: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Practice for Class 7
Addition – Estimated Sum Questions Subtraction – Estimated Difference Questions Multiplication – Estimated Product Questions Division – Estimated Quotient Questions
Indian vs. International Numbering: How Many Zeros Do These Numbers Have?
The content covers the number of zeros in various large numbers, contrasting the Indian and International numbering systems. It poses questions about the zeros in terms like crore, lakh, arab, and kharab for the Indian system, and million, billion, and trillion for the International system.
Ratio & Proportion Problem for Class 6: Saving & Expenditure Quiz
Ratio & Proportion Problem for Class 6: Saving & Expenditure Quiz
Proportion Quiz: Find the Missing Terms!
The Proportion Quiz challenges participants to find missing terms in given proportion problems. It encompasses various questions with set terms and requires calculation of unknown values. Users can submit their answers and reset the quiz while receiving a score based on correct responses. It is an engaging way to practice proportion skills.
Algebra and Arithmetic Operations Quiz for Class 6
The content is about a Class 6 Math Quiz focused on Algebra and Arithmetic Operations. It includes a series of questions that require students to calculate values based on given variables and expressions. The interface allows users to submit answers, check scores, and reset the quiz for practice.
Addition & Subtraction Operations Integer for Class 6 Quiz
Addition & Subtraction Operations Integer for Class 6 Quiz Math Quiz Math Quiz Submit Reset
Problem on Conversion – m, cm & mm for Class 4
The content provides a series of conversion exercises for metric measurements, including converting centimeters to meters, meters to centimeters, meters to millimeters, and millimeters to centimeters. It features various specific values to be converted, demonstrating practical applications of these metric unit conversions across different measurement scales.
Mastering Time Conversion: 12-Hour and 24-Hour Formats
This quiz tests your ability to convert between 12-hour and 24-hour clock formats, ensuring you understand time representation. Practice converting AM/PM times to military time and vice versa. Strengthen your time-reading skills with interactive questions, including morning, afternoon, and midnight conversions. Perfect for students and learners of all ages!
Weight Metric Conversion Problem for Class 4: Fun Exercises
This quiz focuses on converting between kilograms and grams, helping you master weight measurements in the metric system. Practice converting kg to g, g to kg, and mixed units like “kg g” to grams or kilograms. Perfect for students and learners looking to strengthen their understanding of unit conversions in mathematics.
Easy Distance Metric Conversion for Class 4: Practice Examples
This quiz tests your knowledge of unit conversions between kilometers and meters. Practice converting kilometers to meters, meters to kilometers, and mixed values like “3 km 25 m” into different units. Strengthen your understanding of the metric system with these engaging and practical math questions. Try it now and check your answers!
Understanding Clock Time: Before, After, Past, To for Class 4
Solve clock time-based questions involving ‘before,’ ‘after,’ ‘past,’ and ‘to.’
Fraction Word Problems for Class 4: Fun Quiz
Test your fraction skills with this interactive quiz! Solve real-world problems involving fractions, proportions, and percentages. Enter your answers, check if they’re correct, and reset anytime. Perfect for students and learners of all levels. Challenge yourself and improve your understanding of fractions with this fun and engaging exercise!
Decimal Expanded Form for Class 4: Exercises
Test your knowledge of decimal expansion with this interactive quiz! Convert decimal numbers into their expanded forms
Fraction to Decimal for Class 4: A Fun Quiz
This interactive decimal conversion quiz helps users practice converting fractions into decimals. It features 22 questions covering denominators of 10 and 100, with real-time answer validation. Correct answers appear in green, incorrect in red. Users can submit responses and reset the quiz anytime. Perfect for improving decimal understanding and fraction conversion skills!
Solving Fraction Addition Problems – Class 4
Practice your fraction addition skills with this interactive quiz! Solve equations by filling in the missing fractions and calculating sums. Perfect for students and math enthusiasts to improve their understanding of fractions.
Decimal Form Quiz: Mastering Place Values
Test your decimal knowledge with this interactive quiz! Convert word-based number descriptions into decimal form, enter your answers in the input boxes, and check your score with the submit button. Reset anytime with the undo button. A fun and educational way to practice decimals for students and math enthusiasts! 🚀
Master Equivalent, Improper, and Mixed Fraction Conversions
Test your fraction skills with this interactive quiz! Solve equivalent fractions, convert improper fractions to mixed numbers, and vice versa. Enter your answers in the input boxes, check your score with the submit button, and reset with the undo button. Perfect for students and math enthusiasts to practice and improve! 🚀
Test Your Skills: Tenths & Hundredths Decimal Quiz
Test your decimal knowledge with this interactive quiz! Convert decimals to tenths and hundredths by filling in the blanks. Submit your answers to check accuracy, and use the undo button to reset. A fun and educational way to practice fractions and decimals. Try now and improve your math skills!
Master Fraction Equivalence: Take Our Quiz Now!
The content presents a quiz focusing on fraction equivalence, featuring multiple-choice questions on converting fractions to their equivalent forms, decimals, and mixed numbers. It includes options for answers and functions for checking responses and resetting the quiz, with visual feedback based on correctness.
Mastering Decimal Comparisons: Take the Quiz – Class 4
The content presents a decimal quiz with questions regarding identifying the smallest and largest decimals among given options, as well as finding a decimal closest to 0.5. The quiz includes a function for checking answers and a feature to reset answers, displaying the correct count upon submission.
Learn Fractions with a Matching Game – Class 4 Math
The content describes a fraction matching game that involves dragging and matching answers to fill in the blanks for different types of fractions. It includes coding elements for drag-and-drop functionality, with correct answers highlighted in green and incorrect ones in red. The game promotes learning about fractions interactively.
Math Class 4 – Clock Hands & time after and ago
The post presents a series of time-related questions, including drawing clock hands for specific times, calculating future and past times over various intervals, and figuring out what the time will be after specified durations. It involves both visual and mathematical problem-solving with different time frames.
Math Class 4 – Time – 12 hour & 24 hour Clock
The content instructs the reader to calculate specific times in both 12-hour and 24-hour formats based on given scenarios. It includes several time intervals before and after specified times, illustrating the conversion between clock formats. Each scenario prompts a response with the calculated time in both formats.
Math Class 4 – Time -10:15 a.m. and 5:00 p.m.
The content lists various time intervals to be calculated between specified start and end times. Each pair of times, ranging from early morning to late evening, requires determining the duration in hours and minutes, illustrating a practical exercise in time calculation for various scenarios throughout the day.
Agile Coach Interview Question – What metrics do you track to measure the success and effectiveness of Agile implementations?
Velocity measures the amount of work your team can complete in a given sprint, providing valuable insights into your team’s productivity. Cycle time, on the other hand, tracks the time it takes to complete a task, helping you identify and address bottlenecks.
Finally, customer satisfaction is a critical metric that gauges how well your Agile process is meeting the needs of your stakeholders. We’ll discuss how to effectively measure and interpret this data to drive continuous improvement.
By understanding these key Agile success metrics, you’ll be able to make data-driven decisions and ensure your Agile implementation is delivering the desired results. Don’t forget to like and share this video if you found it helpful!
#AgileMetrics #AgileDevelopment #projectmanagementtutorial
Agile Coach Interview Question – What strategies do you use to gain buy-in from stakeholders and leadership for Agile transformations?
To gain buy-in for Agile transformations, educate stakeholders on Agile principles, align practices with organizational goals, share success stories, start with small wins, involve key stakeholders early, provide training, communicate progress, address concerns openly, and celebrate successes. These strategies pave the way for successful Agile adoption across the organization.
Agile Metrics – Lead Time vs Cycle Time
Agile – Lead Time vs Cycle Time
#scrum #scrummaster #scrummasterinterview #agile #leadtime #cycletime #agilecoach
Hardening Sprints in Scrum – A Necessary Evil?
Hardening Sprints in Scrum – A Necessary Evil ?
What is hardening sprint ? Why is hardening sprint – an Agile Anti-pattern?
#hardeningsprint #scrum #scrummaster #scrummasterinterview #agile #scrumantipattern
Scrum Anti-Patterns
Scrum anti-patterns are common deviances from Scrum principles that hinder team effectiveness. Examples include lack of commitment to Sprint Goal, overcommitment, micromanagement, ignoring Definition of Done, lack of transparency, blaming individuals for failures, hero culture, scope creep, sprint cancellations, and resistance to change. Addressing these is vital for fostering continuous improvement and consistent value delivery.
WIP Limit in Scrum
WIP limits in Scrum manage work flow. They encourage completion focus, identify bottlenecks, maintain flow, foster collaboration, and improve predictability. They lead to efficient, transparent, and collaborative teams, resulting in better outcomes and high-quality deliverables.
10 Vocabulary words, meaning & sentence related to personal development, social awareness, and environmental consciousness
Resilience is the ability to recover from setbacks. Diversity involves inclusivity of different cultures. Sustainability means maintaining resources without harm. Innovation introduces new ideas or products. Collaboration entails working together. Empathy is understanding others’ feelings. Adaptability adjusts to new circumstances. Conservation preserves natural resources. Equality ensures equal treatment. Curiosity drives learning and discovery.
Mastering the System Design Interview for Software Development Managers and Technical Program Managers at Amazon
In Amazon’s SDM and TPM interviews, candidates must solve complex business problems with scalable, customer-centric technical solutions. Embracing ambiguity, justifying technical choices, and effective communication are crucial. Efficient time management and practice in presenting ideas within time limits are essential. Mastering these skills is vital for success in the interviews.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the essential link between human language and computer comprehension. It transforms unstructured text, such as spoken language, into structured data that computers can process. NLP is used in machine translation, virtual assistants, sentiment analysis, and spam detection, operating through techniques like tokenization, stemming, and part of speech tagging.
- Class 4
- Class 5
- Class 6
- Competitive Exams
- English
- English Class 1
- English Class 2
- English Class 3
- English Class 4
- English Class 5
- English Class 6
- IEO Olympiad Preparation
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 1
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 2
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 3
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 4
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 5
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 6
- Olympiad English Class 2
- Olympiad Preparation - Class 1 - 10
- SOF Olympiad
- SOF Olympiad - IEO
- Unified Council English Olympiad
- Unified Council Olympiad
Vocabulary – Daily 10 Words – 26 Mar 2024
Today’s vocabulary journey introduces ten words, from familiar to new, emphasizing the importance of repetition for mastery. With meanings and sentences, we explore “serenade,” “gleaming,” “harbor,” “enigma,” “resilient,” “idyllic,” “luminescent,” “traverse,” “spectacle,” and “envision.” Embrace these words to enrich communication and understanding. Happy learning!
- Class 4
- Class 5
- Class 6
- Competitive Exams
- English
- English Class 1
- English Class 2
- English Class 3
- English Class 4
- English Class 5
- English Class 6
- IEO Olympiad Preparation
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 1
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 2
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 3
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 4
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 5
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 6
- Olympiad English Class 2
- Olympiad Preparation - Class 1 - 10
- SOF Olympiad
- SOF Olympiad - IEO
- Unified Council English Olympiad
- Unified Council Olympiad
Vocabulary – Daily 10 Words – 25 Mar 2024
In this vocabulary adventure, we explored words like exuberant, mysterious, vibrant, captivating, idyllic, enchanting, and more. As you incorporate these words into your repertoire, use them thoughtfully and creatively to paint vivid pictures and evoke emotions in your writing. Keep exploring and let language enrich your life!
- Class 6
- Competitive Exams
- English
- English Class 1
- English Class 2
- English Class 3
- English Class 4
- English Class 5
- English Class 6
- IEO Olympiad Preparation
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 1
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 2
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 3
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 4
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 5
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 6
- Olympiad English Class 2
- Olympiad Preparation - Class 1 - 10
- SOF Olympiad
- SOF Olympiad - IEO
- Unified Council English Olympiad
- Unified Council Olympiad
Vocabulary – Daily 10 Words – 24 Mar 2024
This content introduces 10 captivating words, such as “euphoric” and “tranquil,” and provides their meanings and usage in sentences. It encourages readers to expand their vocabulary and express themselves more eloquently. The piece invites readers to continue their exploration of words and promises more content in the future.
Why Product Roadmaps are important?
Product roadmaps are crucial for guiding teams, communicating clearly, and demonstrating commitment to stakeholders and customers. Roadmapping maturity varies from no roadmaps to fully aligned ones. To build successful roadmaps, define the vision, make data-driven decisions, know your audience, select the right roadmap, and tell a compelling story. Integrating roadmaps involves using appropriate tools, involving everyone, sharing progress, and building trust. Avoid myths and adopt best practices to create effective, flexible roadmaps.
- Class 6
- Competitive Exams
- English
- English Class 1
- English Class 2
- English Class 3
- English Class 4
- English Class 5
- English Class 6
- IEO Olympiad Preparation
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 1
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 2
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 3
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 4
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 5
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 6
- Olympiad English Class 2
- Olympiad Preparation - Class 1 - 10
- SOF Olympiad
- SOF Olympiad - IEO
- Unified Council English Olympiad
- Unified Council Olympiad
Vocabulary – Daily 10 Words – 23 Mar 2024
Title: Voyage through Words: A Journey to Expand Your Vocabulary Welcome aboard to an exciting adventure in the realm of words! Are you ready to […]
- Class 4
- Class 5
- Class 6
- Competitive Exams
- English
- English Class 1
- English Class 2
- English Class 3
- English Class 4
- English Class 5
- English Class 6
- IEO Olympiad Preparation
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 1
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 2
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 3
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 4
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 5
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 6
- Olympiad Preparation - Class 1 - 10
- SOF Olympiad
- SOF Olympiad - IEO
- SOF Olympiad Preparation
Vocabulary – Daily 10 Words – 22 Mar 2024
The content provides definitions and sentences for various words.
It includes words like abundant, authentic, dedicate, anticipate, accumulate, adapt, adept, abandon, adhere, and agony, with their meanings and example sentences.
SOF Level 2 Exam Results 2023-2024 are out – IMO, NSO and IEO
SOF Level 2 Results are out now. Please follow below steps to check SOF Level 2 results :
Math Class 3 – Money – Word Problem
Math Class 3 – Money – Word Problem
Math Class 3 – Measurement – Word Problem
Math Class 3 – Measurement – Word Problem
Math Class 3 – Measurement – Fill in the Blanks
Math Class 3 – Measurement – Fill in the Blanks
Math Class 3 – Decimal – Addition & Subtraction – Fill in the Blanks
Math Class 3 – Decimal – Addition & Subtraction – Fill in the Blanks
Math Class 3 – Measurement of Length – Conversion to cm and m
Math Class 3 – Measurement of Length – Conversion to cm and m
Math Class 3 – Money – Exchange Notes – Fill in the Blanks
Math Class 3 – Money – Exchange Notes – Fill in the Blanks
Math Class 3 – Measurement of Mass – KG to G or G to KG – Multiple Choice Question
Math Class 3 – Measurement of Mass – KG to G or G to KG – Multiple Choice Question
Math Class 3 – Money – Addition & Subtraction – Multiple Choice Questions
Math Class 3 – Money – Addition & Subtraction – Multiple Choice Questions
Math Class 3 – Measurement Units – Multiple Choice Questions
Math Class 3 – Measurement Units – Multiple Choice Questions
Math Class 3 – Money Multiple Option Question
Math Class 3 – Money Multiple Option Question
Math Class 5 – Area & Perimeter Word Problem
Math Class 5 – Area & Perimeter Word Problem
Math Class 5 – Define type of angles and draw an example for each type
An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, like a corner of a piece of paper. A right angle is exactly 90 degrees, resembling an L. An obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees, like an open book. A straight line measures 180 degrees, forming a perfectly straight line.
Math Class 5 – Equivalent Fraction
I. Equivalent Fraction II. Equivalent Fraction III. Equivalent Fraction or not
Math Class 5 – Write in fraction and decimal
The given content lists fractions and decimals:
– 23.45 (twenty-three point four five)
– 79.68 (seventy-nine point six eight)
– 42.13 (forty-two point one three)
– 59.26 (fifty-nine point two six)
– 36.79 (thirty-six point seven nine)
– 68.32 (sixty-eight point three two)
– 95.14 (ninety-five point one four)
– 71.05 (seventy-one point zero five)
– 86.97 (eighty-six point nine seven)
– 123.28 (one hundred twenty-three point two eight)
– 14.36 (fourteen point three six)
– 57.89 (fifty-seven point eight nine)
– 30.02 (thirty point zero two)
– 146.75 (one hundred forty-six point seven five)
– 83.41 (eighty-three point four one)
– 483.01 (4 hundred eighty-three point four zero one)
– 108.07 (one hundred eight point zero seven)
Math Class 5 – Fraction & Decimal – Multiple Option Questions
I. Smallest & Greatest fraction with same denominator II. Greatest & smallest fraction with different denominator III. Decimal form of fraction IV. Tenth , Hundredth […]
Math Class 5 – Measurement , Area & Perimeter Problems – Exam Preparation
Math Class 5 – Measurment in length – Conversion ProblemMath Class 5 – Measurement of Mass – Conversion ProblemsMath Class 5 – Measurement of Capacity […]
Math Class 5 – Area and Perimeter Problems
Area & Perimeter Length ( m ) Breadth (m) Area of rectangle ( sq. m ) 10 20 13 156 25 225 Area 9. Write […]
Math Class 5 – Measurement of Time – Addition & Subtraction
I. Time Addition II. Time Addition III. Time Subtraction IV. Time Subtraction
Math Class 5 – Measurement of Time – Conversion Problems
The given content involves converting time measurements between hours, minutes, and seconds. It includes tasks such as converting hours and minutes to minutes, minutes to hours and minutes, minutes and seconds to seconds, and seconds to minutes and seconds. Each conversion requires precision in calculating the time units accurately and effectively.
Math Class 5 – Measure of Mass – Addition Problems
Sarah bought a total of 9 kg 798 g of fruits. Alex purchased a total of 5 kg 70 g of fruits. David bought a total of 15 kg 515 g of fruits. Emma purchased a total of 4 kg 190 g of fruits. James bought a total of 12 kg 210 g of fruits. Lily purchased a total of 14 kg 910 g of fruits. Ethan bought a total of 11 kg 129 g of fruits. Mia purchased a total of 12 kg 304 g of fruits. Jack bought a total of 13 kg 940 g of fruits. Sophia purchased a total of 14 kg 60 g of fruits. Olivia bought a total of 12 kg 130 g of fruits. William purchased a total of 12 kg 120 g of fruits. Ava bought a total of 12 kg 210 g of fruits. Noah purchased a total of 14 kg 65 g of fruits. Isabella bought a total of 12 kg 350 g of fruits.
Math Class 5 – Measurement of Capacity – Conversion Problem
I. Convert ml to l II. Convert l to ml III. Convert l & ml to ml IV. Convert l & ml to l
Math Class 5 – Measurement of Mass – Conversion Problems
The content provides conversion exercises for kilograms (kg) and grams (g). It includes converting various weights from kg to g, kg to kg and g, and g to kg & g. Additionally, it presents the conversion of combined kg and g to kg, as well as standalone g to kg.
Math Class 5 – Measurment in length – Conversion Problem
I. Convert into m II. Convert into km III. Convert from bigger unit Km to smaller unit IV. Convert from bigger unit m to smaller […]
Math Class 3 – Exam Preparation – Division & Fraction
Math Class 3 – Fraction – Half Quiz Math Class 3 – Simple Division Quiz Math Class 3 – Fraction Quarter Fill in the Blanks […]
Math Class 3 – Fraction – Shaded and Unshaded Problem
The task is to calculate the fraction of the shaded and unshaded parts in the given picture.
Math Class 3 – Fraction Word Problem
In the bookstore, 140 magazines are in the fashion category. In the bakery, 288 cupcakes are chocolate flavor. The fruit basket has 320 oranges. The toy store has 100 dolls. In the classroom, 300 students are boys. In the garden, 96 flowers are tulips. The store has 180 red shirts. At the zoo, there are 120 lions. The farmer has 125 roosters. The library has 86 books in English.
Math Class 3 – Divide and check your answer questions
The following division problems were solved and their answers checked: 254 ÷ 6, 378 ÷ 7, 480 ÷ 8, 324 ÷ 6, 560 ÷ 8, 396 ÷ 6, 288 ÷ 8, 450 ÷ 9, 672 ÷ 7, 312 ÷ 6, 504 ÷ 9, 360 ÷ 6, 640 ÷ 8, 252 ÷ 7, 216 ÷ 9.
Math Class 3 – Division & Fraction – Match the following Questions
I.
1) Quarter of 36 is iii) 9
2) 49 ÷ 7 is ii) 7
3) Any number divided by itself is iii) 1
II.
1) Half of 16 is iii) 8
2) Any number divided by same number is iii) 1
3) 36 ÷ 4 is iii) 9
III.
1) 20 ÷ 5 is iii) 4
2) What is remainder – odd number divided by 2 is iii) 1
3) One-third of 15 is i) 5
Math Class 3 – Division Choose correct option
This is a math quiz with division problems and multiple-choice answers. The problems range from simple to complex, involving division of numbers from 72 to 672 by different divisors. The challenge is to select the correct quotient from the given options.
Math Class 3 – Simple Division Fill in the Blanks
The given content contains a series of division problems. Here are the solutions for each:
120 ÷ 4 = 30
84 ÷ 2 = 42
150 ÷ 5 = 30
64 ÷ 8 = 8
108 ÷ 6 = 18
80 ÷ 10 = 8
135 ÷ 9 = 15
72 ÷ 6 = 12
200 ÷ 4 = 50
144 ÷ 12 = 12
Math Class 3 – Fraction Quarter Fill in the Blanks problem
I. Fill in the blanks : II. Fill in the blanks III. Fill in the blanks IV. Fill in the blanks
Math Class 3 – Simple Division Quiz
24 put into equal groups of 6 is 4.
36 divided into equal groups of 9 is 4.
48 shared equally into groups of 12 results in 4.
30 distributed into equal groups of 5 equals 6.
42 split evenly into groups of 7 gives 6.
56 divided into equal groups of 8 yields 7.
63 divided among equal groups of 9 equals 7.
72 shared equally into groups of 6 results in 12.
90 distributed into equal groups of 10 equals 9.
54 split evenly into groups of 9 gives 6.
80 divided into equal groups of 4 yields 20.
Math Class 3 – Fraction – Half Quiz
The content consists of various fill-in-the-blank questions related to finding the half of different numbers, including numerical equations and word problems. It covers basic mathematical concepts of halving numbers and calculating fractions.
English – Interjection – Uses & Examples
Various interjections serve different purposes and are commonly used in everyday language. “Oops!” acknowledges mistakes or mishaps in a light-hearted manner, “Ouch!” expresses sudden pain or discomfort, “Yummy!” conveys delight in tasty food, “Ohh!” signifies surprise, understanding, or appreciation, “Hurray!” celebrates joy and triumph, “Wow!” expresses amazement or admiration, “Oh my god!” signifies intense emotions, “Bravo!” conveys admiration or congratulations, “Hey!” grabs attention or expresses informal greetings and emotions. These interjections add color and meaning to conversations.
CBSE English Class 3 – Fill in the blanks with correct form of singular or plural verb
India plays good cricket. Government takes care of its people. The students study hard for their exams. The cat purrs contentedly while sitting on the windowsill. My family enjoys going on hikes together. The flowers in the garden bloom beautifully in the spring. His glasses need cleaning. The birds in the trees sing melodiously every morning. The team captain leads the players to victory. The children in the playground laugh and play joyfully. The company expands its operations to new markets. The orchestra performs classical music at the concert hall. The book on the shelf falls to the ground with a thud. Our neighbors host a barbecue party every summer. The sun shines brightly in the clear blue sky. My friend invites me to his birthday party. The chef prepares delicious meals for the restaurant patrons.
CBSE English Class 3 – Aladdin and the Magic Lamp – Exam Preparation
The merchant in the story of “Aladdin and the Magic Lamp” asked Aladdin to retrieve a boulder from a cave, where he found the lamp. Aladdin’s refusal to give the lamp to the merchant was due to discovering its unique properties. The genie in the lamp offered Aladdin a wish when he rescued him. The author of the story is unknown.
CBSE Class 5 Science – The Skeletal and Muscular System – Exam Preparation
The content discusses the skeletal and muscular system, covering topics such as cartilage, ligaments, tendons, bone marrow, voluntary and involuntary muscles, ribcage structure, backbone structure, and joints differentiation. It also explores the role of muscles and bones in body movement and whether we can control our heartbeat. A bone and muscle structure labeling is also requested.
CBSE Class 5 Science : Changes in Environment Exam Preparation
Pollution encompasses various types, including acid rain, greenhouse gases, and noise pollution. Air and water pollution result from sources like industrial emissions and chemical runoff, affecting ecosystems and human health. The greenhouse effect drives global warming, caused by human activities. Differentiation between biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste is crucial for waste management.
Demystifying Load Balancing: Ensuring Smooth Sailing for Your Applications
In the bustling world of modern technology, where millions of users interact with applications simultaneously, the concept of load balancing emerges as a crucial mechanism. […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
Common Mistakes in Daily Scrums: Moving Beyond Stand-ups
The daily scrum is essential for team synchronization in agile development. Common pitfalls include misnaming the meeting, treating it as a project report, and allowing it to become lengthy. To enhance effectiveness, stick to the three questions and address deep discussions later. Embracing inclusivity, brevity, and focused discussion empowers teams for project success.
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
Mastering User Stories: A Guide for Product Managers
User Stories are essential narratives guiding product development. They focus on user needs, with a simple format (WHO, WHAT, WHY) and follow the 3 C’s (Card, Conversation, Confirmation). Adhering to the INVEST criteria ensures value and actionability. Breaking down stories into manageable pieces is crucial. Mastering this art empowers Product Managers for success.
Math : Probability Definition – High School
Probability is the likelihood of an event occurring in a given set of conditions, represented by a value between 0 and 1. Event is an individual outcome or set of outcomes in a random experiment. For a die roll event, the probability of obtaining an even number is 1/2. When tossing a coin three times, the probability of at least one Tails appearing is 7/8.
.NET Core – Entity Framework in MVC
Question: What is Entity Framework in MVC and how does it simplify database access in application development? Answer: Entity Framework serves as an object-relational mapper […]
Algebra – Evaluate Functions Quiz
This post contains a quiz with four evaluation function questions. The answers are evaluated using JavaScript and a score is displayed. The evaluation functions are h(t) = -20+11t, g(r) = -3r+10, f(x) = 20 – 35/t, and y(x) = 25 – 6x. The user’s score is displayed after submitting the answers.
Exploring Monolithic vs. Microservices Architecture: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
The discussion explores the differences between monolithic and microservices architecture, each with its advantages and drawbacks. Monolithic architecture offers streamlined development but faces challenges with scaling. In contrast, microservices architecture allows for independent components and enhanced scalability, yet introduces complexities. The choice depends on project nature and scalability needs, balancing agility, and maintainability.
RELEASE TRAIN ENGINEER – LEADERSHIP STYLE
A Release Train Engineer (RTE) in the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) must employ various leadership styles, including servant, facilitative, decisive, coaching, systems thinking, collaborative, Lean-Agile mindset, emotional intelligence, continuous improvement, and inspirational leadership to ensure efficient project management and team success. These attributes contribute to a culture of collaboration, continuous improvement, and value delivery in line with SAFe principles.
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Scrum Master Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
Definition of Ready – Crafting ‘Ready’ User Stories: A Blueprint for Sprint Success
To ensure smooth sprint execution, it’s vital to have “ready” user stories, clear, feasible, and testable. A sample user story for password reset should have acceptance criteria, security measures, scalability, and performance criteria defined. The “Definition of Ready” checklist outlines the necessary criteria for a user story to be considered ready for implementation.
Project Kick Off Meeting
By following these steps, the project kick-off meeting establishes a solid foundation for successful project execution, aligning stakeholders, clarifying objectives, and setting the stage for […]
Understanding Microservices: Distributed Tracing and Log Aggregation
Welcome to our exploration of microservices, distributed tracing, and log aggregation! In this blog, we’ll delve into the fundamental concepts behind these crucial elements of […]
IEO Level 2 Class 1 to 5 – Practice Questions – Prepositions – Part 1
English Quiz: Choose the Correct Option English Quiz: Choose the Correct Option
- IEO Olympiad Preparation
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 1
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 2
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 3
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 4
- IEO Olympiad Preparation - Class 5
- Olympiad Preparation - Class 1 - 10
- SOF Olympiad
- SOF Olympiad - IEO
- SOF Olympiad Preparation
- Uncategorized
IEO Level 2 Class 5 – Practise Questions – Verb Tenses
Quiz: Choose the Correct Option Quiz: Choose the Correct Option
Padma Award Winners 2024
Padma Awards – one of the highest civilian Awards of the country, are conferred in three categories, namely, Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri. […]
Scaling Systems and Essential Design Concepts Explained
Are you aiming to transition from a junior developer to a seasoned pro capable of building scalable applications or perhaps eyeing a substantial pay increase by acing your system design interview? To reach those heights, you’ll need more than just coding skills – you’ll need a comprehensive understanding of essential system design concepts. Let’s delve into some key ideas and strategies that can propel your technical prowess to the next level
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
A Day in the Life of a Technical Program Manager
As a Program Manager, my daily routine is a delicate dance between reacting to immediate needs and proactively driving long-term initiatives. In this blog post, […]
Technical Program Manager or Engineering Manager Interview questions : Tell me about me your leadership style you use
In the realm of successful leadership, adaptability in employing different leadership styles is crucial. I don’t adhere to a single leadership approach; rather, I tailor […]
Technical Program Management: What does it take to be a wildly successful TPM?
Let’s delve into the fundamental aspects. TPM Skills can be categorized into three domains, each encompassing a range of skillsets. Domain 1️⃣: Excellence in Program […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
TPM Interview Question – As a Technical Program Manager, how would you handle a situation were critical and blocker bug is reported one day before the launch ?
Handling a critical and blocker bug reported just one day before a launch is a challenging situation that requires a swift and well-coordinated response. Here’s […]
TPM Interview Questions – How to isolate bottlenecks in System Design ?
Identifying and isolating bottlenecks in system design is a crucial aspect of ensuring optimal performance. Here are steps you can take to identify and address […]
TPM Interview Questions – How to handle a situation where team member from another team is hesitant to work on your program
Handling a situation where a team member from another team is hesitant to work on your program requires a combination of empathy, effective communication, and […]
SOF 2023-2024 – NSO, IEO, IGKO, IMO, ISSO, ICO and NCO Exam Result
School Olympiad Foundation (SOF) conducts the National Science Olympiad (NSO), International English Olympiad (IEO), International General Knowledge Olympiad (IGKO), International Mathematics Olympiad (IMO), International Social […]
IEO Olympiad Preparation Class 1 to 5 – Singular and Plural
Singular-plural question paper: Section A: Singular or Plural? Instructions: For each sentence, choose the correct form of the noun (singular or plural) to complete the […]
IGKO Preparation Class 1 to 5 – Location
The Great Barrier Reef, the world’s largest coral reef system, is located in which country? Machu Picchu, the ancient Incan citadel, is situated in which […]
Padma Award Winner List – 2023
Padma Award Winner List – 2023 Padma Vibhushan Recepients List Name Field State/Country 1. Shri Balkrishna Doshi (Poshumous) Others Gujarat 2. Shri Dilip Mahalanabis (Posthumous) […]
Time Basic Quiz – Class 1 Onwards
Time Basic Quiz – Class 1 Onwards
Number Divisibility Rules
The post explains the divisibility rules for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, and 10. It provides examples and problems to test understanding, such as determining divisible numbers and checking divisibility by 4 and 8 without actual division.
संयुक्त व्यंजन
संयुक्त व्यंजन दो व्यंजन के संयुक्त रूप को कहते हैं जैसे- क्ष, त्र, ज्ञ, श्र संयुक्त व्यंजन की हिंदी वर्णमाला में कुल संख्या 4 है जो की निम्नलिखित […]
Place Value – Greatest & Smallest Numbers – Grade/Class 4
The greatest 4 digit number without repeating the digits is __________________________________ The greatest 4 digit number with repeating the digits is ___________________________ The smallest 4 […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical IT Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
Program Status Meeting
Apart from running regular daily standup meetings with development/engineering team, it is important to run Program Status Meeting involving engineering, program management, product management , […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
Portfolio – Project Selection and Prioritisation
Portfolio – Project Selection and Prioritisation As Portfolio / Program Manager, you will have lot of projects in your project backlog. As an effective Portfolio/Program […]
Olympiad Preparation – Class 3 – Weekly Questions – 3 Oct Week
Addition , Subtraction and Expanded Form Questions for Class 3 Olympiad Aspirants Parents/Kids, We plan to publish 9 Olympiad Questions each week to prepare your […]
Punctuation and Capital Letters
Punctuation There are 14 punctuation marks that are commonly used in English grammar. They are the period, question mark, exclamation point, comma, semicolon, colon, dash, […]
JAVA and OOPs Concepts
Object Oriented Programming Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of “objects”, which can contain data and code: data in the form of fields (often known as attributes or properties), and […]
Difference between Procedural and Object Oriented Programming
Procedural Oriented Programming Object Oriented Programming In procedural programming, program is divided into small parts called functions. Example code : #include <stdio.h>/*this function computes the absolute […]
Pronoun
What is a pronoun? A pronoun is a word used instead of a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns refer to either a noun that has already been mentioned […]
Adjective : Describing Words
What is an Adjective?Adjective describes a noun hence they are called describing words.They tell us many things about a noun (shape, size, colour, age, number, […]
SINGULAR AND PLURAL NOUN : ONE AND MANY
SINGULAR AND PLURAL NOUN : ONE AND MANY Words which name only ONE person, place, animal or thing are called SINGULAR nouns.Words which name MANY […]
VERBS : ACTION WORDS
What is a verb? Verbs are words that describe actions, whether physical or mental. It expresses the action done by the noun or pronoun in […]
USE OF A and AN VOWELS and CONSONANTS
ARTICLES A and AN is used when we speak of one person, place, animal or thing. AN is used before naming words that begin with […]
Noun
What is a noun? A noun is a word that names something, such as a person, place, thing, or idea. In a sentence, nouns can […]
Place Value of Two Digit Numbers – Quiz
UKG, Class 1 and Class 2 Place Value of Two Digit Numbers – Example Number : 3 2 Place Value of 3 is 30 Place Value of 2 is 2 Solve below problem: The place value […]
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 24 May to 30 May 2021 for Competitive Exams
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 24 May to 30 May 2021 for Competitive Exams Current Affairs 1. New CBI Director Senior IPS officer Subodh Kumar Jaiswal […]
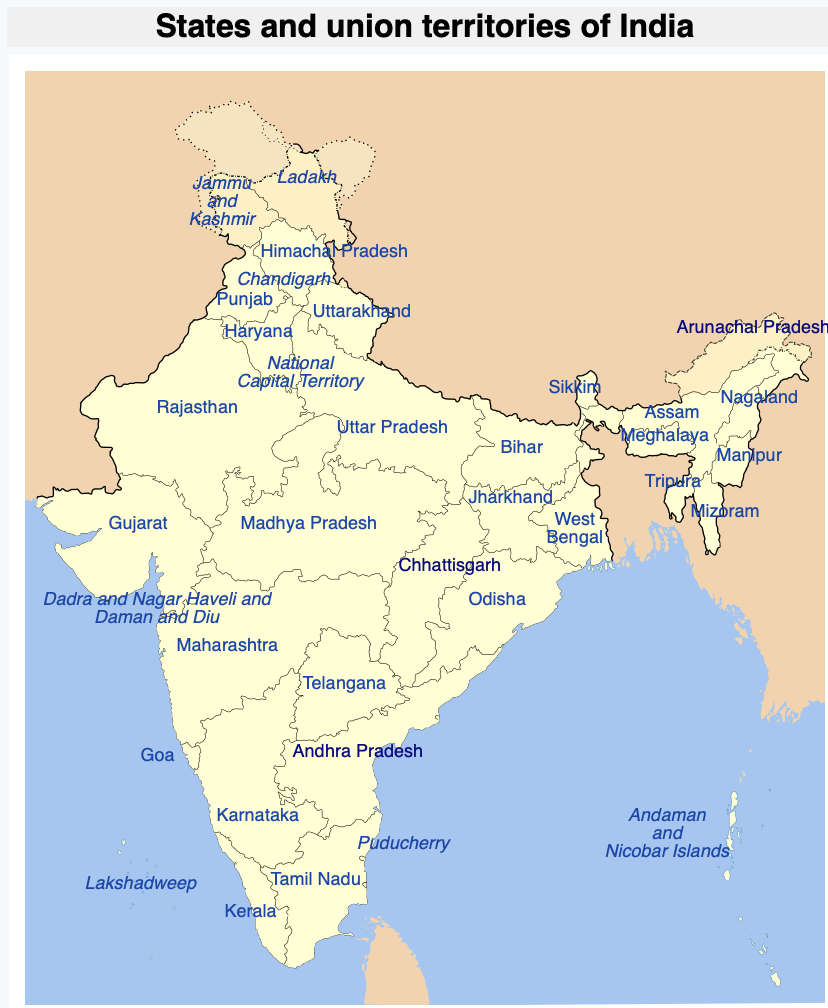
States , Union Territories and Official Language of India 2021
States , Union Territories and Official Language of India 2021 There are 28 states in India. State Official Additional official languages[39] languages[39] Andhra Pradesh […]
Machine Learning Interview/Quiz Questions
Machine Learning Interview/Quiz Questions Machine Learning Interview/Quiz Questions Click on Questions to reveal the answer Which function in Pandas library allows to manipulate data and […]
States , Union Territories and Capitals of India 2021
States , Union Territories and Capitals of India 2021 There are 28 states in India. S.No States Name Capital Formed on 1 Andhra Pradesh Visakhapatnam(executive)Amaravati (legislative)Kurnool (judicial) […]
MARRS PRESCHOOL BEE – ENGLISH NATIONALS JUNIOR KG SAMPLE PAPER
MARRS PRESCHOOL BEE – ENGLISH NATIONALS JUNIOR KG SAMPLE PAPER SECTION 1 – Forming Words Using The Letter Given. Question 1. Forming Words Using The […]
Mental Ability – Competitive Exam Preparation – Number Series by adding fixed number – NTSE, NCO, NSO, IMO and other Competitive Exams
Mental Ability – Competitive Exam Preparation – Number Series by adding fixed number – NTSE, NCO, NSO, IMO and other Competitive Exams The sequence or […]
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 10 May to 16 May 2021 for Competitive Exams
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 10 May to 16 May 2021 for Competitive Exams Current Affairs Dr. Tahera Qutbuddin has become the first person from India […]
Complete Word by Identifying the Picture Part 1 Quiz – LKG, UKG and Class 1
Complete Word by Identifying the Picture Part 1 – LKG, UKG and Class 1 Exam Preparation for English Olympiad and Spell Bee
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 3 May to 9 May 2021 for Competitive Exams
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 3 May to 9 May 2021 for Competitive Exams Current Affairs Mayflower 400Mayflower 400 is the world’s first Artificial Intelligence Ship, […]
Ascending and Descending Numbers for Olympiad Exam – IMO etc – Class 3
Ascending and Descending Numbers for Olympiad Competitive Exam – IMO etc – Class 3 Which of below options shows number is descending order ? 2. […]
Human Body Blood Notes for Competitive Exams
Human Body Blood Notes for Competitive Exams Blood is fluid connective tissue pH of blood is 7.4 pH is a scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of […]
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 26 April to 2 May 2021 for Competitive Exams
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 26 April to 2 May 2021 for Competitive Exams Oscar Winners Announced The winners were announced at the 93rd Annual Academy […]
Crack Maths Olympiad – Calendar Problem – Class 1 and 2
Maths Olympiad – Calendar Problem – Class 1 and 2 1. Duggu celebrates his birthday on Wednesday in June. Which of below dates is surely […]
Addition of numbers upto 10 – Counting Objects – Interactive Math Worksheet LKG and UKG
Addition of numbers upto 10 – Counting Objects – Interactive Math Worksheet LKG and UKG Addition of numbers upto 10 – Counting Objects – Math […]
Arrange in Ascending Order – Upto 20 – Math Worksheet – LKG and UKG – Interactive Worksheets
Arrange in Ascending Order – Upto 20 – Math Worksheet – LKG and UKG
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 19 April to 25 April 2021 for Competitive Exams
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz: 19 April to 25 April 2021 1. Idriss Déby, one of Africa’s longest-serving leaders passed away on April 20th. He was the […]
Odd and Even Number Exercises for Class 2 and Class 3 Students
Write all odd numbers between 786 to 800 Write all even numbers between 200 and 220 Write all odd numbers between 343 and 352 Write […]
National Level Science Talent Search Examination- NSTSE – CLASS 2 QUESTION 2021 – PART 3
National Level Science Talent Search Examination- NSTSE – CLASS 2 QUESTION 2021 – PART 3 Look at the picture and answer question no. 21 – […]
Fill in the missing letters (4 or 5 letter words)
Fill in the missing letters (4 or 5 letter words) Spell Bee preparation for LKG and UKG Students 1. R __ A D 2. D […]
Antonyms Online Quiz for Kids
Antonyms Online Quiz for Kids Prepare your kid for English School and Competitive Exams
National Level Science Talent Search Examination- NSTSE – CLASS 2 QUESTION 2021 – PART 1
National Level Science Talent Search Examination- NSTSE – CLASS 2 QUESTION 2021 – PART 1 01. Which option represents the grouping ? 02. Mona wrote […]
Duggu n Dakshu TV -Popular Recent Post
Duggu n Dakshu TV -Popular Recent Post Math Worksheet LKG and UKG – Comparing Number – Greater than ( > ), Less than ( < […]
GLOSSARY OF CRICKET TERMS – OLMYPIAD GENERAL KNOWLEDGE PREPARATION – CLASS 1 to 5
Arm Ball A ball bowled by a slow bowler which has no spin on it and so does not turn as expected but which stays on […]
Real Numbers Types – Rational and Irrational – Math Cheatsheet – Class 9 and 10
Chart – Number Systems Real Numbers Rational Numbers ( Example : -9, 0 , 5/7, 2/5 etc ) Integers ( Example : -2 , -1 […]
Unified International Mathematics Olympiad – UIMO – CLASS 2 QUESTION 2020 – PART 1
Unified International Mathematics Olympiad – UIMO – CLASS 2 -QUESTION 2020 – PART 1 01. Which of the following number statements is incorrect? (A) 234 […]
JUNIOR KG ENGLISH INTERSCHOOL SPELL BEE SECOND ROUND-Complete Missing Letter in Series
JUNIOR KG ENGLISH INTERSCHOOL SPELL BEE SECOND ROUND-Complete Missing Letter in Series COMPLETE THE MISSING LETTER IN THE SERIES 1. E , ____ , G, […]
Olympiad Math Preparation – Class 2 – Pictograph – Part 1
Olympiad Math Preparation – Class 2 – Pictograph – Part 1 1. If stands for 4, then for ________ ? a. 12 b. 16 c. […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
Product Metrics and KPI to Forecast Business Sucess of Product
Metrics to forecast business success of a product 1. Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) These metrics measure a product’s total revenue in one month. What are […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
5 Product Management Online Resources
5 Product Management Online Resources Product Manager HQ – https://productmanagerhq.com Roman Pichler Blog – https://www.romanpichler.com 280Group – https://280group.com Mind the Product – https://www.mindtheproduct.com Product Coalition […]
MATHS FACTS : Addition or Subtraction of Numbers – Part 1
MATHS FACTS : Addition or Subtraction of Numbers – Part 1 Remember 1. 0 added to a number gives same number 0 + 0 = […]
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 5
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 5CLASS : 2 Select the correct option to answer every question given below. Class […]
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 4
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 4CLASS : 2 Select the correct option to answer every question given below. Class […]
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 3
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 3CLASS : 2 Select the correct option to answer every question given below. Class […]
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 2
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 2CLASS : 2 Select the correct option to answer every question given below. Class […]
Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 – Class 2 Examination Papers – Part 1
The content contains examination questions for the Unified Cyber Olympiad 2020 for Class 2. It includes questions related to mental ability, number bonds, arithmetic operations, shapes, and counting. Topics covered include numbers, pictures, shapes, counting, and basic arithmetic.
JUNIOR KG ENGLISH INTERSCHOOL SPELL BEE SECOND ROUND-Sample paper
JUNIOR KG ENGLISH INTERSCHOOL SPELL BEE SECOND ROUND-Sample paper 1. COMPLETE THE MISSING LETTER of the word W _ N T E R A) A B) I C) […]
Olympiad English – Class 2 – Picture Quiz – Nouns
Olympiad IEO – Class 2 -Identify Picture – Nouns Identify noun which describes picture Question 1 : a. Cricket b. Hockey b. Baseball d. Football […]
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – Place value using Abacus – Number up to 20
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – Place value using Abacus – Number up to 20 Abacus also called a counting frame, is […]
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – Count blocks and write correct number
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – Count blocks and write correct number Youtube Video Facebook Video Click the Download button to download […]
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – COUNTING AND COMPARING NUMBERS – Greater than, Less than and Equal to
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – COUNTING AND COMPARING NUMBERS – Greater than, Less than and Equal to Youtube Quiz Video Facebook […]
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – Fill Number Series Up to 20
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG – Fill Number Series Up to 20 Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the Download button […]
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG COMPARING NUMBERS Greater than, Less than and Equal to
Math Tutorial & Quiz for LKG and UKG COMPARING NUMBERS Greater than, Less than and Equal to Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the […]
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Subtraction of Numbers Up to 10 – Using Fingers
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Subtraction of Numbers Up to 10 – Using Fingers Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the Download […]
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG Addition of Numbers Up to 10 Using Fingers
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG Addition of Numbers Up to 10 Using Fingers Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the Download button to […]
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Subtract of Numbers Up to 10 – Draw, Cross and Count Lines
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Subtract of Numbers Up to 10 – Draw, Cross and Count Lines Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video […]
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Subtraction of Numbers Up to 10 – Using Number Line
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG Subtraction of Numbers Up to 10 Using Number Line Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the Download button […]
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Addition of Numbers Up to 10 – Using Number Line
Math Quiz for LKG and UKG – Addition of Numbers Up to 10 – Using Number Line Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the […]
Math Quiz – Addition of Numbers Up to 10 – Draw and Count Lines – LKG and UKG kids
Math Quiz – Addition of Numbers Up to 10 – Draw and Count Lines – LKG and UKG kids Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video […]
Math Quiz on Subtraction of Numbers Up to 10 – Crossing and Counting objects – LKG and UKG
Math Quiz on Subtraction of Numbers Up to 10 – Crossing and Counting objects – LKG and UKG Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click […]
Math Quiz on Addition of Numbers Up to 10 Counting objects for LKG and UKG
Math Quiz on Addition of Numbers Up to 10 Counting objects for LKG and UKG Youtube Quiz Video Facebook Quiz Video Click the Download button […]
Olympiad Math Exam Preparation – Class 1 – Number Sense
Olympiad Math Exam Preparation – Class 1 Number Sense Identify numbers and their names – Up to 100 After, Before and Between Numbers – Up to 100 […]
Olympiad Math Preparation – Class 2 – Number Sense
Olympiad Math Preparation – Class 2 Number Sense Numerals and Number Names (3 digits) Comparing Numbers Ascending or Descending Order Abacus and Place Value Even […]
Math Worksheet LKG, UKG, Grade 1 and Grade2 – Days of Week
The worksheet involves arranging the days of the week in the correct order, identifying the number of days in a week, completing given patterns, and answering questions regarding the sequence and relationship between different days. It concludes with an option to download the free worksheet PDF.
Math Worksheet LKG, UKG, Grade 1 and Grade2 – Write missing number in addition by Crossing and Counting Objects – Number up to 10
Math Worksheet LKG, UKG, Grade 1 and Grade2 – Writemissing number in addition by Crossing and Counting Objects – Number up to 10 Click the […]
Math Worksheet – UKG, Grade 1 and Grade 2 – Clock Time
Math Worksheet – UKG, Grade 1 and Grade 2 – Clock Time Write Clock Time ________ o’clock ________ o’clock […]
Math Worksheet UKG, Grade 1 and Grade2 – Write missing number in addition – Number up to 100
Math Worksheet UKG, Grade 1 and Grade2 – Write missing number in addition – Number up to 100 Write missing number 20 + ______ […]
Math Worksheet LKG and UKG – ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION – 1 MORE or 1 LESS – Number up to 20
Math Worksheet LKG and UKG – ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION – 1 MORE or 1 LESS – Number up to 20 1 more or 1 […]
Math Worksheet UKG, Grade 1 and Grade 2 – ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION – 10 MORE or 10 LESS – Number up to 100
Math Worksheet UKG, Grade 1 and Grade 2 – ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION – 10 MORE or 10 LESS – Number up to 1000 10 […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
What is purpose of Product Roadmap
Product Roadmap helps create alignment across different functions. It helps align engineering , sales, marketing, human resource , legal and product management team towards product […]
Who are stakeholders for Product Roadmap
Complete product stakeholders for Product Roadmap are listed below. Depending on product you are managing , some of them might be optional and not required 1. […]
What is R ?
R R is free open source language. It is used statistical and visualisation software. It can handle both structure and unstructured data Features of R […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
Database Capacity Estimation for Technical Program Manager or Technical Product Manager
To determine a database Capacity Estimation , we will consider BookmyShow.com as example Requirements of BookmyShow.Com Functional Requirements: Our ticket booking service should be able […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
Software Architecture – Web Application Technical Terminologies for Technical Product Manager and Program Manager
Software Architecture – Web Application Technical Terminologies for Technical Product Manager and Program Manager 1. Scalability Scalability means the ability of the application to handle […]
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
WIREFRAMING TOOLS FOR PRODUCT MANAGERS
WIREFRAMING TOOLS FOR PRODUCT MANAGERS Axure RP iRise Balsamiq UXPin InVision MockingBird Adobe XD JustinMind OmniGraffle
How do JSON Web Tokens work?
How do JSON Web Tokens work? The application or client requests authorization to the authorization server. This is performed through one of the different authorization […]
Cluster Analysis
Cluster Analysis Cluster analysis from Jewel Refran
Which assembly is used to define ASP.NET MVC Framework
System.Web.Mvc assembly contains all classes and interfaces to support ASP.NET MVC Framework
Enable Fill Handle in Microsoft Excel
Enable Fill Handle in Microsoft Excel Open Microsoft Excel and then click on File -> Options. Click Advanced, and then under Editing options, select the […]
Enable or Disable fill handle in Excel
Enable or Disable fill handle in Excel One can turn this option on or off by following below steps: Click the Microsoft Office Button , and then […]
Unable to install .NET Framework 4.5 using dotNetFx45_Full_setup.exe installer without internet connection in server
Error : Unable to install .NET Framework 4.5 using dotNetFx45_Full_setup.exe installer without internet connection in server Resolution : dotNetFx45_Full_setup.exe installer is web installer for .NET […]
Where to define AutoEventWireup attribute in ASP.NET
One can specify AutoEventWireup attribute in the following locations: • The Machine.config file • The Web.config file • Individual Web Forms (.aspx files) • Web […]
What is AutoEventWireup attribute in ASP.NET
AutoEventWireup attribute is set to false by default in the .aspx page and event handlers are automatically created. When you set the value of the […]
.NET components call COM components.
.NET Components can call COM components The proxy used in calling unmanaged code from managed code is known as a Runtime-Callable Wrapper, or RCW. Ways […]
New Features of VB.NET and C# languages in 2005 version
New Features of VB.NET and C# languages in 2005 version VB.NET C# Visual Basic 2005 has many new and improved language features — such as […]
AJAX Poll Questions
What is default value of UpdateMode property of ASP.NET UpdatePanel control ? 1. Always 2. Conditional 3. Partial 4. Never Please provide right answer […]
What is metrics in project management
A metric is a value you use to measure your product’s quality. ExampleSchedule VarianceDefect Density
Introduction to ASP.NET MVC using C#
Getting Started Start by running Visual Studio 2010 and select New Project from the Start page. Visual Studio 2010 – Start Page Creating Your […]
ADO.NET Data Row Version values
ADO.NET Data Row Version values DataRowVersion value Description Current The current values for the row. This row version does not exist for rows with a […]
ADO.NET Row State Versus Row Versions
Row state indicates the status of a row whereas Row versions maintain the values stored in a row as it is modified, including current, original, and […]
How can user locale information accessed in Asp.net application
Question : How can user locale information accessed in Asp.net application Answer : Using System.Web.UI.Page.Culture property
Is visual studio required to write .NET program ?
Is visual studio required to write .NET program? Answer : No .Net program can be written in notepad and compiled in command prompt
Write a C# code to get list of parent ASP.NET controls from Child ASP.NET controls
C# code to get list of parent ASP.NET controls from Child ASP.NET controls private ArrayList WalkthroughContainers(Control ctl) { ArrayList retContainers = new ArrayList(); Control parent […]
What are various value of RowState of ADO.NET DataRow object ?
Values of RowState of ADO.NET DataRow object : Sl No RowState value Description 1 Unchanged No changes have been made. 2 Added The row has […]
Explain RowState property in ADO.NET DataRow object ?
RowState property of DataRow object determines the current state of the row. Various RowState values are : Unchanged , Added , Modified , Deleted , […]
Naming Conventions -C# Coding Guidelines
C#.NET Coding Guidelines Naming Conventions 1. Prefix member variables with the underscore ‘_’. 2. Do not prefix member variables with “this”.3. Use camelCasing for member […]
Write a Validation Expression for RegularExpressionValidator to allow letters , numbers , space , dash and underscore
Question : Write a Validation Expression for RegularExpressionValidator to allow letters , numbers , space , dash and underscore ? Answer : ValidationExpression=”^([a-zA-Z0-9_s-]*)$” Explanation : […]
Error : ORA-01460: unimplemented or unreasonable conversion requested
Error ORA-01460: unimplemented or unreasonable conversion requested Error Details Getting the above error when trying to pass byte array of size greater than 32 K […]
ASP.NET MVC Design
ASP.NET MVC Design ASP.NET MVC Design ASP.NET MVC Design pattern derives from MVC design pattern i.e. Model View Controller design pattern. It seperates […]
Microsoft Web Platform Installer
Microsoft Web Platform Installer Microsoft Web Platform Installer (Web PI) is a free tool that makes getting the latest components of the Microsoft Web Platform, […]
Setting Menu options Dynamically based on Role in ASP.NET using LINQ
Setting Menu options Dynamically based on Role in ASP.NET using LINQ Step 1. Add Menu control to aspx or master page. <asp:Menu ID=”menuRoleBased” runat=”server” Font-Names=”Verdana” […]
ASP.NET , C# – Configuring to use XML to display error and validation message
ASP.NET , C# – Configuring to use XML to display error and validation message Step 1 – Add XML file to store error and validation […]
AJAX Client Side Event Life Cycle
AJAX Client Side Event Life Cycle 1. Page Request 2. Init 3. Load · initializeRequest · beignRequest · pageLoading · pageLoaded 4. Load · endRequest […]
SOA Principles
SOA Principles Service-oriented architecture ( SOA ) is based on the four fundamental tenets that follow: 1. Explicit Boundaries Everything needed by the service to […]
What is ScriptManager ?
ScriptManager ScriptManager control on a page is used to enable the Microsoft Ajax features of ASP.NET: Client-script functionality of the Microsoft Ajax Library, Partial-page rendering, […]
- Agile Articles
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Scrum Master Interview Questions
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- Uncategorized
Important Scrum Terminology
The content discusses essential terminology and roles in Scrum methodology. It defines key elements such as Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and relevant meetings like Daily Scrum, Sprint Planning, Retrospective, and Review. Additionally, it outlines Scrum roles including Product Owner, ScrumMaster, Team, Stakeholder, Pig, and Chicken. This comprehensive guide provides insights into the Scrum framework.
Project Management : What is Fishbone diagram or Ishikawa diagram or Cause and effect diagram ?
Fishbone diagram or Ishikawa diagram or Cause and effect diagram Fishbone diagram or Ishikawa diagram or Cause and effect diagram are used to show causes […]
Programming with word in C# : Replace bookmark with actual values
Programming with word in C# : Replace bookmark with actual values Step 1 : Add a bookmark to work document ( for example StudentLetter.doc ) […]
Dropdown : Use FindByText or FindByValue to select item in dropdown
Dropdown : Use FindByText or FindByValue to select item in dropdown You have added a dropdownlist to webpage with ID = ddlAccomodations Avoid using : ddlAccomodations.SelectedValue […]
Webservice Questions : Difference between web services & remoting?
Difference between web services & remoting? 1) Protocol : Webservice can be accessed over HTTP protocol . Remoting can be accessed over any protocol (including […]
WCF Questions : What is WCF ?
What is WCF ? WCF stands for Windows Communication Foundation. WCF was introduced with .NET Framework 3.0. It provides combined features of Web Services , […]
What’s the Difference Between and ?
We can use two constructs to access page-level variables in an ASP.NET web template: data binding syntax Data binding—the hierarchical mapping of control properties to […]
Portfolio , Program and Projects
Portfolio is collection of programs and projects. Program is group of related projects. Project is temporary body of work that produces unique service or product or […]
Securing View State in ASP.NET
Securing View State in ASP.NET View state data is stored in the web page in a hidden field and is encoded using base64 encoding. In addition, […]
Quick Links Quick Links WCF Tutorial Service Oriented Architecture ( SOA ) WCF Introduction WCF Contracts Hosting WCF Service WCF Contract Attributes WCF Tools Support […]
Quick Links Quick Links WCF Tutorial Service Oriented Architecture ( SOA ) WCF Introduction WCF Contracts Hosting WCF Service WCF Contract Attributes WCF Tools Support […]
C# FAQS Class Various class modifiers are listed below : new public protected internal private abstract sealed static Class – new modifier The new modifier […]
WCF Tutorial Service Oriented Architecture ( SOA ) WCF Introduction WCF Contracts Hosting WCF Service WCF Contract Attributes WCF Tools Support Serialization and Encoding in […]
Serialization and Encoding in WCF
Serialization and Encoding in WCF An important part of communication between WCF Applications is Serialization . Serialization and deserialization are processes involved in converting objects […]
WCF – Windows Communication Foundation
WCF – Windows Communication Foundation Introduction .NET Framework 3.0 introduces four important features : Windows Communication Foundation ( WCF ) Windows Presentation Foundation ( WPF […]
C# Partial Methods
C# Partial Methods Partial methods can be defined in one part of a type declaration and implemented in another. The implementation is optional; if no […]
Process for Implementing Triggers and Timers
Process for Implementing Triggers and Timers An UpdatePanel control on your page will update (through a partial-page postback operation) when a control that it contains […]
ASP.NET AJAX Components
ASP.NET AJAX has 2 main components: AJAX Library – This runs on the client AJAX Extensions – This runs on the server. Interview Questions .NET […]
Service-Oriented Architecture ( SOA )
Service-Oriented Architecture ( SOA ) Introduction: In today’s technology-driven world with globalization, rapid business changes and with ever growing challenges posed by integration between globally […]
ASP.NET Web Application Security
ASP.NET with IIS, can authenticate user credentials such as names and passwords using any of the following authentication methods: •Windows: Basic, digest, or Integrated Windows […]
Cross Page Posting in ASP.NET Page
The Server.Transfer method can be used to move between webpages. This does not change the URL In ASP.NET 2.0 , cross page posting feature was […]
- .NET Interview Questions
- Product Management
- Product Management Interview Questions
- Product Owner Interview Questions
- Program Management
- Project Management
- Project Management Articles
- Project Management Interview Questions
- SQL Server Articles
- Technical Program Management
- Technical Program Management - Interview Questions
- TechnicalProgramManagement
- TPM Interview Questions
SQL Server 2005 Enhancements
New features in SQL 2005 in brief: SQL Server 2005 as .NET runtime host: enhancing security, reliability, and performance Writing procedures, functions, and triggers in […]
ASP.NET Error Handling and Tracing
ASP.NET TraceASP.NET introduces tracing functionality which allows one to view diagnostic information about a single request for an ASP.NET page simply by enabling it for […]
Understanding ASP.Net Configuration settings
The properties and behavior of the ASP .Net application are determined by the settings contained within the specific files called as the configuration files. There […]
Exception Handling in .NET
Introduction Exception handling is made easier and streamlined in .Net. It uses the Exception objects to cascade the exception between layers and allows handling them […]
ASP.NET Application Deployment
ASP.NET Application Deployment Once an application has been developed and tested ,application is ready for deployment to client machines. The goal of deployment is the […]
LINQ to ADO.NET
LINQ to ADO.NET A .NET application can write LINQ queries to SQL, Entities and Dataset. LINQ to SQL and LINQ to Entities have direct connection […]
.NET Remoting
Application domain The boundary with in which .NET application runs. Application domain provides isolated environment for a .NET application. Application running in one application domain […]
ASP.NET Tutorial : Getting started with ASP.NET
This ASP.NET tutorial provides a quick start to creating dynamic web applications. The steps include opening Visual Studio, creating a new website, adding a label control, and running the web site. This concise guide sets the stage for getting started with ASP.NET development in Microsoft Visual Studio 2008.